Table of Contents
What is a Mobile App?
Mobile app refers to a software application developed for smartphones and tablets that offers various functions and services to users.
Mobile apps allow consumers to perform myriad activities, retrieve any required data, and interact with services instantly. You can download such apps from different app shops like Apple’s App Store and Google Play Store.
- Instagram
Instagram is one of the best social media apps, where you can share pictures and photos. This mobile app provides access to creative tools and filters to make mobile users easily engage. The key features of Instagram mobile app includes IGTV for longer videos, direct messaging and photo editing tools.
- Uber
Uber introduced an easy-to-use mobile application that completely changed the way consumers request transportation services. Users can order rides, track drivers in real time, and make cashless payments using this application on their mobile phone. This mobile application transformed how we think about transportation by easing urban commuting.
For example,
After learning the definition of mobile apps, let’s discuss the types of mobile apps.
4 Major Types of Mobile Apps
Here are the 4 major types of mobile apps.
Native Apps
Native apps are custom-built for certain operating systems like iOS and Android. These native apps are famous for providing high performance and smooth integration with the hardware of the device.
Native apps have access to device functions like the camera and push notifications to provide users with rich and immersive experiences. These apps can be found in app stores tailored to particular operating systems, for instance, the App Store for iOS apps or Google Play for Android apps.
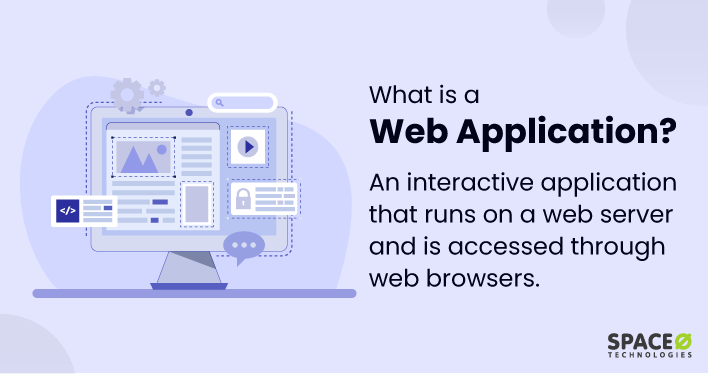
Web Apps
Web applications are very practical because you can start using them on your mobile web browser immediately. These apps are easy to access and use compared to native apps, which you install on your device. Compared to a native app, a web-based app is directly accessible on web browsers.
This way, you get instant access to services online like news feeds, social media platforms, productivity tools, and cloud storage. These apps are your preferred companions when you require instant access to details or services as long as you have an internet connection.
- Web app examples – Gmail, Google Docs, Trello, and Asana
Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps combine the best features of native and web apps. These apps are built with web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript yet are not enclosed within a native container. Here, developers can save time and resources by writing code once and deploying it across numerous platforms.
A Hybrid app provides a close-to-native user experience and has access to device functionalities. These apps are free to download from app stores and provide an equal amount of cross-platform compatibility with native-like performance.
- Hybrid apps example – UberEats, Amazon, Microsoft Teams, and Twitter
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
Progressive web apps are like pioneers in mobile technology, bridging the gaps between native and web apps. These apps provide the convenience of web access while also including functionality often associated with native apps.
PWAs can be operated in the background, providing push notifications, and even be integrated into your device’s home screens for easy access. This innovative approach is changing the future of mobile engagement by combining speed, convenience, and creativity.
- Progressive web app examples – Forbes, Pinterest, Flipkart, and AliExpress
- Native apps examples – Spotify, Facebook, Snapchat, and WhatsApp
Now that you have an overview of the types of mobile apps, if you still want to gain more information, you can check out our complete guide on different types of mobile apps. Next, let’s discuss the pros and cons of mobile apps.
Pros and Cons of Mobile Apps
Here are the pros and cons associated with mobile apps.
| Pros of Mobile Apps | Cons of Mobile Apps |
|---|---|
| Mobile applications provide a more dynamic and intuitive user interface than mobile webpages, giving a better user experience. | Particularly for several platforms (iOS and Android), developing and maintaining mobile apps may be expensive. |
| Many apps let users access material and conduct tasks when not connected to the internet, improving accessibility and usability even in regions with little or no internet connection. | One major challenge is attracting users as noticing the mobile app in the app store where millions of apps already exist becomes difficult. |
| Just because native apps are optimized for particular platforms and devices, these apps are efficient to use. | The requirement of regular upgrades to repair issues and add new features requires constant resources and effort. |
| Mobile apps can leverage device features like GPS, camera, and notifications, enhancing functionality and enabling innovative use cases. | |
| Apps offer a direct channel for businesses to engage with users, build brand loyalty, and deliver personalized content and promotions. |
These were the advantages and limitations. If you want to understand each advantage in detail, you can check out our blog post on the advantages of mobile apps for businesses. Now, let’s discuss how mobile apps work.
How Do Mobile Apps Actually Work?
Here is a step-by-step explanation of how mobile apps work.
- The UI designers are responsible for developing the visual elements of the apps. The UI designers ensure that the mobile app is efficient and enjoyable to use. The UI phase involves user flows, navigation, and accessibility features.
- UX designers are concerned with the complete user journey within the app. UX graphics designers ensure that the software is easy to use, efficient, and fun. Designing user flows, navigation and accessibility features are all part of this.
- Developers write the code that allows the application to function. These experts provide functionality based on UI and UX designs by using Java, Swift, Kotlin, or JavaScript. This phase involves creating interactive features and dealing with user input.
- Many mobile apps need to communicate with remote servers or external services in real time. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) make this interaction possible by permitting the mobile application to obtain data, transmit updates, or synchronize user information.
- Developers offer regular updates to maintain smooth operation and security. These updates include bug fixes, performance improvements, new features, or compatibility changes.
Mobile apps consist of two parts:
Front-end: The front end (client side) is where users directly interact on their devices.
Back-end: The back end (server side) is responsible for the logic of the application and handling data.
A mobile app is a software application targeted at smartphones and tablets. Users receive different features and services through these mobile applications. There are four types of mobile apps that include a native app known for its high performance, a web-based app for instant online access, hybrid apps combining web and native app features, and PWAs pushing mobile technology forward.